代理:设计模式
代理是一种常用的设计模式,其目的就是为其他对象提供一个代理以控制对某个对象的访问。代理类负责为委托类预处理消息,过滤消息并转发消息,以及进行消息被委托类执行后的后续处理
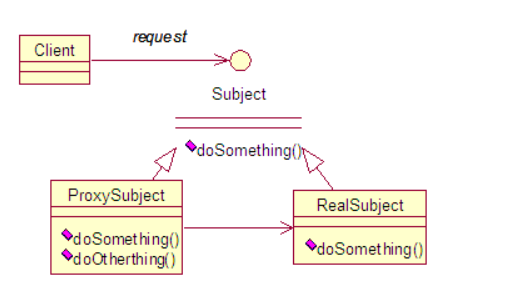
相关的类和接口
动态代理机制的主类
java.lang.reflect.Proxy:这是 Java 动态代理机制的主类,它提供了一组静态方法来为一组接口动态地生成代理类及其对象
方法一
该方法用于获取指定代理对象所关联的调用处理器
1 | /** |
方法二
该方法用于获取关联于指定类装载器和一组接口的动态代理类的类对象
1 | /** |
方法三
该方法用于判断指定类对象是否是一个动态代理类
1 | /** |
方法四
该方法用于为指定类装载器、一组接口及调用处理器生成动态代理类实例
1 | /** |
调用处理器接口
java.lang.reflect.Proxy:这是 Java 动态代理机制的主类,它提供了一组静态方法来为一组接口动态地生成代理类及其对象
核心方法
该方法负责集中处理动态代理类上的所有方法调用。第一个参数既是代理类实例,第二个参数是被调用的方法对象
第三个方法是调用参数。调用处理器根据这三个参数进行预处理或分派到委托类实例上发射执行
1 | public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) |
创建动态代理
版本一
实现 InvocationHandler 接口
通过实现 InvocationHandler 接口创建自己的调用处理器
创建动态代理类
通过为 Proxy 类指定 ClassLoader 对象和一组 interface 来创建动态代理类
获得动态代理类的构造函数
通过反射机制获得动态代理类的构造函数,其唯一参数类型是调用处理器接口类型
创建动态代理类实例
通过构造函数创建动态代理类实例,构造时调用处理器对象作为参数被传入
代码
1 | // InvocationHandlerImpl 实现了 InvocationHandler 接口,并能实现方法调用从代理类到委托类的分派转发 |
版本二
简化的动态代理对象创建过程
代码
1 | // InvocationHandlerImpl 实现了 InvocationHandler 接口,并能实现方法调用从代理类到委托类的分派转发 |
使用java动态代理
Demo1
编写接口
Advice.java
1 | package com.zbiti.proxy; |
编写接口实现类
AdviceImpl.java
1 | package com.zbiti.proxy; |
测试
ProxyTest.java
1 | package com.zbiti.proxy; |
结果:
1 | end |
Demo2
手动实现一个数据库连接池, 没有使用代理模式的情况下如下:
MyPool.java
1 | package com.zbiti.proxy; |
使用代理模式
MyPool2.java
1 | package com.zbiti.proxy; |

