涉及技术介绍
Hibernate
Your relational data. Objectively. - Hibernate ORM
Object/Relational Mapping
Hibernate ORM enables developers to more easily write applications whose data outlives the application process. As an Object/Relational Mapping (ORM) framework, Hibernate is concerned with data persistence as it applies to relational databases (via JDBC). Unfamiliar with the notion of ORM? Read here.
JPA Provider
In addition to its own “native” API, Hibernate is also an implementation of the Java Persistence API (JPA) specification. As such, it can be easily used in any environment supporting JPA including Java SE applications, Java EE application servers, Enterprise OSGi containers, etc.
Idiomatic persistence
Hibernate enables you to develop persistent classes following natural Object-oriented idioms including inheritance, polymorphism, association, composition, and the Java collections framework. Hibernate requires no interfaces or base classes for persistent classes and enables any class or data structure to be persistent.
High Performance
Hibernate supports lazy initialization, numerous fetching strategies and optimistic locking with automatic versioning and time stamping. Hibernate requires no special database tables or fields and generates much of the SQL at system initialization time instead of at runtime.
Hibernate consistently offers superior performance over straight JDBC code, both in terms of developer productivity and runtime performance.
Scalability
Hibernate was designed to work in an application server cluster and deliver a highly scalable architecture. Hibernate scales well in any environment: Use it to drive your in-house Intranet that serves hundreds of users or for mission-critical applications that serve hundreds of thousands.
Reliable
Hibernate is well known for its excellent stability and quality, proven by the acceptance and use by tens of thousands of Java developers.
Extensibility
Hibernate is highly configurable and extensible.
JPA 标准
Java Persistence API - Wikipedia
The Java Persistence API (JPA) is a Java application programming interface specification that describes the management of relational data in applications using Java Platform, Standard Edition and Java Platform, Enterprise Edition.
Persistence in this context covers three areas:
- the API itself, defined in the
javax.persistencepackage - the Java Persistence Query Language (JPQL)
- object/relational metadata
Hibernate JPA
Hibernate 在3.2 以后根据JPA 规范提供了一套操作持久层的 API
Spring Data
Spring Data’s mission is to provide a familiar and consistent, Spring-based programming model for data access while still retaining the special traits of the underlying data store.
It makes it easy to use data access technologies, relational and non-relational databases, map-reduce frameworks, and cloud-based data services. This is an umbrella project which contains many subprojects that are specific to a given database. The projects are developed by working together with many of the companies and developers that are behind these exciting technologies.
Spring Data JPA
Spring Data JPA, part of the larger Spring Data family, makes it easy to easily implement JPA based repositories. This module deals with enhanced support for JPA based data access layers. It makes it easier to build Spring-powered applications that use data access technologies.
Implementing a data access layer of an application has been cumbersome for quite a while. Too much boilerplate code has to be written to execute simple queries as well as perform pagination, and auditing. Spring Data JPA aims to significantly improve the implementation of data access layers by reducing the effort to the amount that’s actually needed. As a developer you write your repository interfaces, including custom finder methods, and Spring will provide the implementation automatically.
Spring Data Redis
Spring Data Redis, part of the larger Spring Data family, provides easy configuration and access to Redis from Spring applications. It offers both low-level and high-level abstractions for interacting with the store, freeing the user from infrastructural concerns.
Spring 整合 Hibernate
导入jar包
spring jar包
spring-ioc
spring-beans-4.2.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-context-4.2.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-core-4.2.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-expression-4.2.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-aop
aopalliance.jar
aspectjrt.jar
aspectjweaver.jar
spring-aop-4.2.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-aspects-4.2.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-jdbc
spring-jdbc-4.2.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-tx-4.2.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-orm
spring-orm-4.2.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-test
spring-test-4.2.0.RELEASE.jar
apache-logging
commons-logging-1.1.1.jar
hibernate jar包
hibernate-core
antlr-2.7.7.jar
dom4j-1.6.1.jar
geronimo-jta_1.1_spec-1.1.1.jar
hibernate-commons-annotations-5.0.1.Final.jar
hibernate-core-5.0.7.Final.jar
hibernate-jpa-2.1-api-1.0.0.Final.jar
jandex-2.0.0.Final.jar
javassist-3.18.1-GA.jar
jboss-logging-3.3.0.Final.jar
mysqql-driver
mysql-connector-java-5.1.7-bin.jar
c3p0连接池
c3p0-0.9.2.1.jar
hibernate-c3p0-5.0.7.Final.jar
mchange-commons-java-0.2.3.4.jar
spring整合hibernate
编写配置文件
- 配置读取properties文件的工具类
- 配置c3p0数据库连接池
- 配置Hibernate的SeesionFactory
- 配置Hibernate的事务管理器
- 配置开启注解事务处理
- 配置springIOC的注解扫描
applicationContext.xml
1 |
|
hibernate完成CRUD
创建数据库
编写实体类
Users.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.pojo; |
修改配置文件
添加 HibernateTemplate,修改applicationContext.xml配置文件
1 | <!-- 配置HiberanteTemplate对象 --> |
编写接口
UsersDao.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.dao; |
编写实现类
UsersDaoImpl.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.dao.impl; |
编写测试代码
UsersDaoImplTest.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
HQL查询
HQL:Hibernate Query LanguageHQL的语法:就是将原来的 sql语句中的表与字段名称换成对象与属性的名称就可以了
修改接口
添加查询方法
1 | List<Users> selectUserByName(String username); |
修改实现类
实现查询方法
1 |
|
编写测试代码
测试HQL查询
1 | /** |
SQL查询
修改接口
添加查询方法
1 | List<Users> selectUserByNameUseSQL(String username); |
修改实现类
实现查询方法
1 |
|
编写测试代码
测试SQL查询
1 | /** |
QBC查询
QBC:Query By Criteria
修改接口
添加查询方法
1 | List<Users> selectUserByNameUseCriteria(String username); |
修改实现类
实现接口查询方法
1 |
|
编写测试代码
测试QBC查询
1 | /** |
Spring整合Hibernate JPA
JPA:由 Sun公司提供了一对对于持久层操作的标准(接口+文档)Hibernate:是 Gavin King开发的一套对于持久层操作的自动的ORM框架。Hibernate JPA:是在Hibernate3.2版本那种提供了对于 JPA的标准的实现。提供了一套按
照 JPA 标准来实现持久层开发的 API
导入jar包
在项目中导入 HIbernateJPA相关的 jar
hibernate-entitymanager-5.0.7.Final.jar
修改配置文件
修改applicationContext.xml配置文件
- 配置读取properties文件的工具类
- 配置c3p0数据库连接池
- Spring整合JPA 配置EntityManagerFactory
- 配置jpa的事务管理器
- 配置开启注解事务处理
- 配置springIOC的注解扫描
1 |
|
Hibernate JPA的CRUD
编写实体类
Users.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.pojo; |
编写接口
UsersDao.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.dao; |
编写实现类
UsersDaoImpl.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.dao.impl; |
编写测试代码
UsersDaoImplTest.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
HQL查询
修改接口
添加HQL查询方法
1 | List<Users> selectUserByName(String username); |
修改实现类
实现HQL查询接口方法
1 |
|
修改测试代码
测试HQL查询
1 | /** |
SQL查询
修改接口
添加SQL查询方法
1 | List<Users> selectUserByNameUseSQL(String username); |
修改实现类
实现SQL查询接口方法
1 |
|
修改测试代码
测试SQL查询
1 | /** |
QBC查询
修改接口
添加QBC查询方法
1 | List<Users> selectUserByNameUseCriteria(String username); |
修改实现类
实现QBC查询接口方法
1 |
|
修改测试代码
测试QBC查询
1 | /** |
Spring Data JPA
Spring Data JPA:Spring Data JPA 是spring data项目下的一个模块。提供了一套基于JPA
标准操作数据库的简化方案。底层默认的是依赖 Hibernate JPA来实现的。Spring Data JPA的技术特点:我们只需要定义接口并集成Spring Data JPA中所提供的接
口就可以了。不需要编写接口实现类。
入门
导入jar包
在spring整合hibernate、hibernate JPA的基础jar包上添加
- spring-data-commons-1.11.0.RELEASE.jar
- spring-data-jpa-1.9.0.RELEASE.jar
- slf4j-api-1.6.1.jar
- slf4j-log4j12-1.7.2.jar
- log4j-1.2.16.jar
修改配置文件
JPA命名空间xmlns:jpa="http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa"Spring Data JPA的配置<jpa:repositories base-package="com.bjsxt.dao"/>
1 |
|
编写DAO
1 | package com.bjsxt.dao; |
编写测试代码
JUnit单元测试,事务默认是回滚的
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
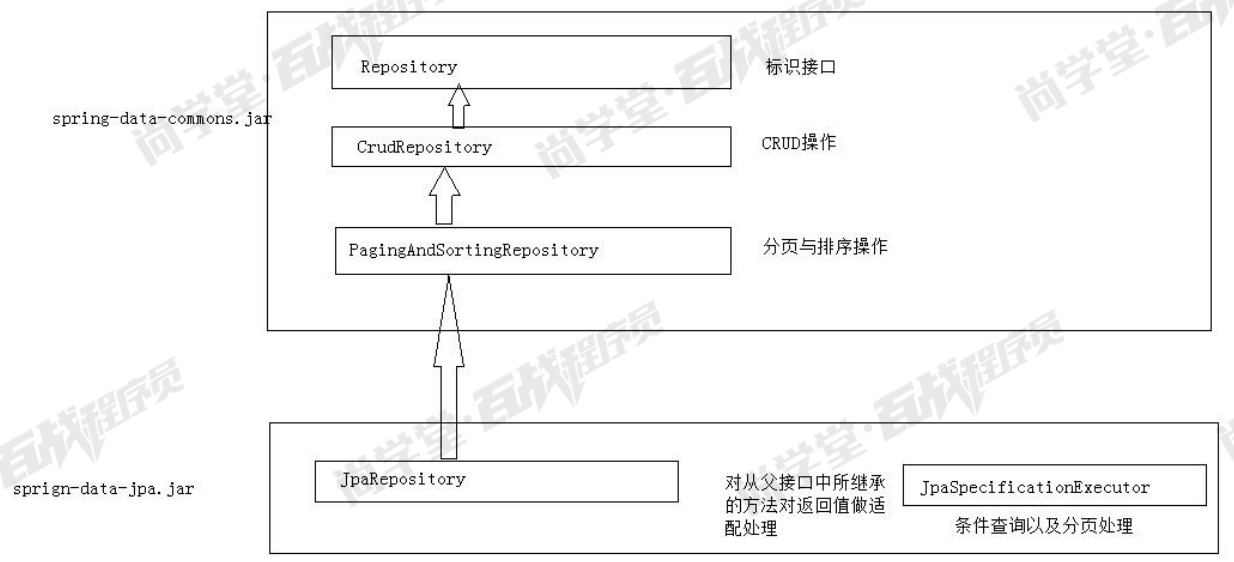
接口继承结构
运行原理
- 入门编写测试代码时,我们注入了接口
UsersDao,自己并没有实现save但是可以直接调用,实际上通过工厂对象JpaRepositoryFactory帮我们生成了代理对象
1 | (name="entityManagerFactory") |
Repository接口
Repository 接口是 Spring Data JPA 中为我我们提供的所有接口中的顶层接口Repository提供了两种查询方式的支持
- 基于方法名称命名规则查询
- 基于
@Query注解查询
方法名称命名规则查询
- 规则:
findBy(关键字)+属性名称(属性名称的首字母大写)+查询条件(首字母大写)
| 关键字 | 方法命名 | sql where 子句 |
|---|---|---|
| And | findByNameAndPwd | where name= ? and pwd =? |
| Or | findByNameOrSex | where name= ? or sex=? |
| Is,Equal | findById,findByIdEquals | where id= ? |
| Between | findByIdBetween | where id between ? and ? |
| LessThan | findByIdLessThan | where id < ? |
| LessThanEqual | findByIdLessThanEquals | where id <= ? |
| GreaterThan | findByIdGreaterThan | where id > ? |
| GreaterThanEqual | findByIdGreaterThanEquals | where id > = ? |
| After | findByIdAfter | where id > ? |
| Before | findByIdBefore | where id < ? |
| IsNull | findByNameIsNull | where name is null |
| isNotNull,NotNull | findByNameNotNull | where name is not null |
| Like | findByNameLike | whre name like ? |
| NotLike | findByNameNotLike | where name not like ? |
| StartingWith | findByNameStartingWith | where name like ‘?%’ |
| EndingWith | findByNameEndingWith | where name like ‘%?’ |
| Containing | findByNameContaining | where name like ‘%?%’ |
| OrderBy | findByIdOrderByXDesc | where id=? order by x desc |
| Not | findByNameNot | where name <> ? |
| In | findByIdIn(Collection<?> c) | where id in (?) |
| NotIn | findByIdNotIn(Collection<?> c) | where id not in (?) |
| True | findByAaaTue | where aaa = true |
| False | findByAaaFalse | where aaa = false |
| IgnoreCase | findByNameIgnoreCase | where UPPER(name)=UPPER(?) |
编写接口
UsersDao.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.dao; |
编写测试类
RepositoryTest.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
@Query 注解的查询
JPQL语句查询
JPQL:通过 Hibernate 的HQL演变过来的。他和 HQL语法及其相似
编写接口
@Query(value="from Users where username = ?")—>表:实体对象,字段:属性
UsersDao.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.dao; |
编写测试类
RepositoryTest.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
SQL语句查询
- 原生
SQL书写方式,nativeQuery=true表示不转义SQL
编写接口
UsersDao.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.dao; |
编写测试类
RepositoryTest.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
@Query注解的更新
编写接口
1 | package com.bjsxt.dao; |
编写测试类
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
CrudRepository接口
编写接口
UsersDao.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.dao; |
编写测试类
RepositoryTest.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
PagingAndSortingRepository接口
分页
编写接口
UsersDao.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.dao; |
编写测试代码
RepositoryTest.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
排序
编写接口
UsersDao.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.dao; |
编写测试代码
RepositoryTest.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
JpaRepository接口
JpaRepository接口是我们开发时使用的最多的接口。其特点是可以帮助我们将其他接口
的方法的返回值做适配处理。可以使得我们在开发时更方便的使用这些方法。
编写接口
UsersDao.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.dao; |
编写测试类
RepositoryTest.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
JpaSpecificationExecutor接口
完成多条件查询,并且支持分页与排序
单条件查询
编写接口
JpaSpecificationExecutor<Users>:不能单独使用,需要配合着jpa中的其他接口一起使用
UsersDao.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.dao; |
编写测试类
RepositoryTest.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
多条件查询
方式一
编写接口
UsersDao.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.dao; |
编写测试类
RepositoryTest.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
方式二
编写接口
UsersDao.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.dao; |
编写测试类
RepositoryTest.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
分页
编写接口
UsersDao.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.dao; |
编写测试类
RepositoryTest.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
排序
编写接口
UsersDao.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.dao; |
编写测试类
RepositoryTest.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
分页与排序
编写接口
UsersDao.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.dao; |
编写测试类
RepositoryTest.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
自定义 Repository 接口
编写接口
UsersRepository.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.dao; |
使用接口
UsersDao.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.dao; |
编写接口实现类
UsersDaoImpl.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.dao; |
编写测试类
RepositoryTest.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
多表操作
一对一
需求:用户与角色的一对一的关联关系
用户:一方
角色:一方
编写Users实体
Users.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.pojo; |
编写Roles实体
1 | package com.bjsxt.pojo; |
编写测试类
OneToOneTest.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
一对多
需求:从角色到用户的一对多的关联关系
角色:一方
用户:多方
编写Users实体
Users.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.pojo; |
编写Roles实体
Roles.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.pojo; |
编写测试类
OneToManyTest.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
多对多
双向的一对多
需求:一个角色可以拥有多个菜单,一个菜单可以分配多个角色。多对多的关联关系
角色:多方
菜单:多方
编写Roles实体
Roles.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.pojo; |
编写Menus实体
Menus.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.pojo; |
编写测试类
ManyToManyTest.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
Spring Data Redis
Spring Data Redis, part of the larger Spring Data family, provides easy configuration and access to Redis from Spring applications. It offers both low-level and high-level abstractions for interacting with the store, freeing the user from infrastructural concerns.
安装
环境
Redis 版本:3.0.0
环境:Linux
步骤
安装 gcc 编译器
1 | yum install gcc-c++ |
解压安装包
1 | tar -zxf redis-3.0.0.tar.gz |
进入解压目录进行编译
1 | cd redis-3.0.0 |
将 Redis 安装到指定目录
1 | make PREFIX=/usr/local/redis install |
启动 Redis
前置启动
1
默认的是前置启动:./redis-server
后置启动
- 先将 redis.conf 文件拷贝到 redis 的安装目录
cp redis.conf /usr/local/redis/bin - 编辑 redis.conf 文件修改:
daemonize yes - 启动:
./redis-server redis.conf - 查看 redis 进程:
ps aux|grep redis - 关闭后置启动的 Redis:
./redis-cli shutdown
- 先将 redis.conf 文件拷贝到 redis 的安装目录
搭建整合环境
创建项目
导入jar包
spring-ioc
spring-beans-4.2.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-context-4.2.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-core-4.2.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-expression-4.2.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-aop
aopalliance.jar
aspectjrt.jar
aspectjweaver.jar
spring-aop-4.2.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-aspects-4.2.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-jdbc
spring-jdbc-4.2.0.RELEASE.jar(这里没有用到)
spring-tx-4.2.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-orm
这里不需要用到
spring test
spring-tx-4.2.0.RELEASE.jar
apache-logging
commons-logging-1.1.1.jar
spring-data-redis
commons-pool2-2.3.jar
jedis-2.7.2.jar
spring-data-redis-1.6.0.RELEASE.jar
编写配置文件
- 配置读取properties文件的工具类
- Jedis连接池
- Jedis连接工厂:创建Jedis对象的工厂
- Redis模板对象:是SpringDataRedis提供的用户操作Redis的对象
applicationContext.xml
1 |
|
redis.properties
1 | redis.pool.maxtTotal=20 |
编写测试类
RedisTest.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
存储实体对象
编写实体类
要实现序列化接口Serializable
Users.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.pojo; |
编写测试类
默认序列化StringRedisSerializer在配置文件applicationContext.xml中指定,测试的时候可以更换序列化器
RedisTest.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |
以 JSON格式存储对象
导入jar包
jackson-annotations-2.8.0.jar
jackson-core-2.8.10.jar
jackson-databind-2.8.10.jar
编写实体类
实现序列化接口
Users.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.pojo; |
编写测试类
设置json序列化器this.redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Users.class));
RedisTest.java
1 | package com.bjsxt.test; |

