代理:设计模式
代理是一种常用的设计模式,其目的就是为其他对象提供一个代理以控制对某个对象的访问。代理类负责为委托类预处理消息,过滤消息并转发消息,以及进行消息被委托类执行后的后续处理
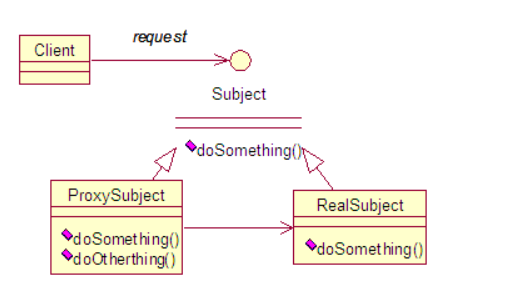
相关的类和接口
动态代理机制的主类
java.lang.reflect.Proxy:这是 Java 动态代理机制的主类,它提供了一组静态方法来为一组接口动态地生成代理类及其对象
方法一
该方法用于获取指定代理对象所关联的调用处理器
/**
* Returns the invocation handler for the specified proxy instance.
*
* @param proxy the proxy instance to return the invocation handler for
* @return the invocation handler for the proxy instance
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the argument is not a
* proxy instance
* @throws SecurityException if a security manager, <em>s</em>, is present
* and the caller's class loader is not the same as or an
* ancestor of the class loader for the invocation handler
* and invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess
* s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to the invocation
* handler's class.
*/
@CallerSensitive
public static InvocationHandler getInvocationHandler(Object proxy)
throws IllegalArgumentException
{
/*
* Verify that the object is actually a proxy instance.
*/
if (!isProxyClass(proxy.getClass())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("not a proxy instance");
}
final Proxy p = (Proxy) proxy;
final InvocationHandler ih = p.h;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
Class<?> ihClass = ih.getClass();
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
if (ReflectUtil.needsPackageAccessCheck(caller.getClassLoader(),
ihClass.getClassLoader()))
{
ReflectUtil.checkPackageAccess(ihClass);
}
}
return ih;
}方法二
该方法用于获取关联于指定类装载器和一组接口的动态代理类的类对象
/**
* Returns the {@code java.lang.Class} object for a proxy class
* given a class loader and an array of interfaces. The proxy class
* will be defined by the specified class loader and will implement
* all of the supplied interfaces. If any of the given interfaces
* is non-public, the proxy class will be non-public. If a proxy class
* for the same permutation of interfaces has already been defined by the
* class loader, then the existing proxy class will be returned; otherwise,
* a proxy class for those interfaces will be generated dynamically
* and defined by the class loader.
*
* <p>There are several restrictions on the parameters that may be
* passed to {@code Proxy.getProxyClass}:
*
* <ul>
* <li>All of the {@code Class} objects in the
* {@code interfaces} array must represent interfaces, not
* classes or primitive types.
*
* <li>No two elements in the {@code interfaces} array may
* refer to identical {@code Class} objects.
*
* <li>All of the interface types must be visible by name through the
* specified class loader. In other words, for class loader
* {@code cl} and every interface {@code i}, the following
* expression must be true:
* <pre>
* Class.forName(i.getName(), false, cl) == i
* </pre>
*
* <li>All non-public interfaces must be in the same package;
* otherwise, it would not be possible for the proxy class to
* implement all of the interfaces, regardless of what package it is
* defined in.
*
* <li>For any set of member methods of the specified interfaces
* that have the same signature:
* <ul>
* <li>If the return type of any of the methods is a primitive
* type or void, then all of the methods must have that same
* return type.
* <li>Otherwise, one of the methods must have a return type that
* is assignable to all of the return types of the rest of the
* methods.
* </ul>
*
* <li>The resulting proxy class must not exceed any limits imposed
* on classes by the virtual machine. For example, the VM may limit
* the number of interfaces that a class may implement to 65535; in
* that case, the size of the {@code interfaces} array must not
* exceed 65535.
* </ul>
*
* <p>If any of these restrictions are violated,
* {@code Proxy.getProxyClass} will throw an
* {@code IllegalArgumentException}. If the {@code interfaces}
* array argument or any of its elements are {@code null}, a
* {@code NullPointerException} will be thrown.
*
* <p>Note that the order of the specified proxy interfaces is
* significant: two requests for a proxy class with the same combination
* of interfaces but in a different order will result in two distinct
* proxy classes.
*
* @param loader the class loader to define the proxy class
* @param interfaces the list of interfaces for the proxy class
* to implement
* @return a proxy class that is defined in the specified class loader
* and that implements the specified interfaces
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if any of the restrictions on the
* parameters that may be passed to {@code getProxyClass}
* are violated
* @throws SecurityException if a security manager, <em>s</em>, is present
* and any of the following conditions is met:
* <ul>
* <li> the given {@code loader} is {@code null} and
* the caller's class loader is not {@code null} and the
* invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPermission
* s.checkPermission} with
* {@code RuntimePermission("getClassLoader")} permission
* denies access.</li>
* <li> for each proxy interface, {@code intf},
* the caller's class loader is not the same as or an
* ancestor of the class loader for {@code intf} and
* invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess
* s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to {@code intf}.</li>
* </ul>
* @throws NullPointerException if the {@code interfaces} array
* argument or any of its elements are {@code null}
*/
@CallerSensitive
public static Class<?> getProxyClass(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>... interfaces)
throws IllegalArgumentException
{
final Class<?>[] intfs = interfaces.clone();
final SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
checkProxyAccess(Reflection.getCallerClass(), loader, intfs);
}
return getProxyClass0(loader, intfs);
}方法三
该方法用于判断指定类对象是否是一个动态代理类
/**
* Returns true if and only if the specified class was dynamically
* generated to be a proxy class using the {@code getProxyClass}
* method or the {@code newProxyInstance} method.
*
* <p>The reliability of this method is important for the ability
* to use it to make security decisions, so its implementation should
* not just test if the class in question extends {@code Proxy}.
*
* @param cl the class to test
* @return {@code true} if the class is a proxy class and
* {@code false} otherwise
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code cl} is {@code null}
*/
public static boolean isProxyClass(Class<?> cl) {
return Proxy.class.isAssignableFrom(cl) && proxyClassCache.containsValue(cl);
}方法四
该方法用于为指定类装载器、一组接口及调用处理器生成动态代理类实例
/**
* Returns an instance of a proxy class for the specified interfaces
* that dispatches method invocations to the specified invocation
* handler.
*
* <p>{@code Proxy.newProxyInstance} throws
* {@code IllegalArgumentException} for the same reasons that
* {@code Proxy.getProxyClass} does.
*
* @param loader the class loader to define the proxy class
* @param interfaces the list of interfaces for the proxy class
* to implement
* @param h the invocation handler to dispatch method invocations to
* @return a proxy instance with the specified invocation handler of a
* proxy class that is defined by the specified class loader
* and that implements the specified interfaces
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if any of the restrictions on the
* parameters that may be passed to {@code getProxyClass}
* are violated
* @throws SecurityException if a security manager, <em>s</em>, is present
* and any of the following conditions is met:
* <ul>
* <li> the given {@code loader} is {@code null} and
* the caller's class loader is not {@code null} and the
* invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPermission
* s.checkPermission} with
* {@code RuntimePermission("getClassLoader")} permission
* denies access;</li>
* <li> for each proxy interface, {@code intf},
* the caller's class loader is not the same as or an
* ancestor of the class loader for {@code intf} and
* invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess
* s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to {@code intf};</li>
* <li> any of the given proxy interfaces is non-public and the
* caller class is not in the same {@linkplain Package runtime package}
* as the non-public interface and the invocation of
* {@link SecurityManager#checkPermission s.checkPermission} with
* {@code ReflectPermission("newProxyInPackage.{package name}")}
* permission denies access.</li>
* </ul>
* @throws NullPointerException if the {@code interfaces} array
* argument or any of its elements are {@code null}, or
* if the invocation handler, {@code h}, is
* {@code null}
*/
@CallerSensitive
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>[] interfaces,
InvocationHandler h)
throws IllegalArgumentException
{
Objects.requireNonNull(h);
final Class<?>[] intfs = interfaces.clone();
final SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
checkProxyAccess(Reflection.getCallerClass(), loader, intfs);
}
/*
* Look up or generate the designated proxy class.
*/
Class<?> cl = getProxyClass0(loader, intfs);
/*
* Invoke its constructor with the designated invocation handler.
*/
try {
if (sm != null) {
checkNewProxyPermission(Reflection.getCallerClass(), cl);
}
final Constructor<?> cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams);
final InvocationHandler ih = h;
if (!Modifier.isPublic(cl.getModifiers())) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {
public Void run() {
cons.setAccessible(true);
return null;
}
});
}
return cons.newInstance(new Object[]{h});
} catch (IllegalAccessException|InstantiationException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
Throwable t = e.getCause();
if (t instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) t;
} else {
throw new InternalError(t.toString(), t);
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e);
}
}调用处理器接口
java.lang.reflect.Proxy:这是 Java 动态代理机制的主类,它提供了一组静态方法来为一组接口动态地生成代理类及其对象
核心方法
该方法负责集中处理动态代理类上的所有方法调用。第一个参数既是代理类实例,第二个参数是被调用的方法对象
第三个方法是调用参数。调用处理器根据这三个参数进行预处理或分派到委托类实例上发射执行
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable;创建动态代理
版本一
实现 InvocationHandler 接口
通过实现 InvocationHandler 接口创建自己的调用处理器
创建动态代理类
通过为 Proxy 类指定 ClassLoader 对象和一组 interface 来创建动态代理类
获得动态代理类的构造函数
通过反射机制获得动态代理类的构造函数,其唯一参数类型是调用处理器接口类型
创建动态代理类实例
通过构造函数创建动态代理类实例,构造时调用处理器对象作为参数被传入
代码
// InvocationHandlerImpl 实现了 InvocationHandler 接口,并能实现方法调用从代理类到委托类的分派转发
// 其内部通常包含指向委托类实例的引用,用于真正执行分派转发过来的方法调用
InvocationHandler handler = new InvocationHandlerImpl(..);
// 通过 Proxy 为包括 Interface 接口在内的一组接口动态创建代理类的类对象
Class clazz = Proxy.getProxyClass(classLoader, new Class[] { Interface.class, ... });
// 通过反射从生成的类对象获得构造函数对象
Constructor constructor = clazz.getConstructor(new Class[] { InvocationHandler.class });
// 通过构造函数对象创建动态代理类实例
Interface Proxy = (Interface)constructor.newInstance(new Object[] { handler });
版本二
简化的动态代理对象创建过程
代码
// InvocationHandlerImpl 实现了 InvocationHandler 接口,并能实现方法调用从代理类到委托类的分派转发
InvocationHandler handler = new InvocationHandlerImpl(..);
// 通过 Proxy 直接创建动态代理类实例
Interface proxy = (Interface)Proxy.newProxyInstance( classLoader,
new Class[] { Interface.class },
handler );使用java动态代理
Demo1
编写接口
Advice.java
package com.zbiti.proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public interface Advice {
void forwardMethod(Method method);
void backMethod(Method method);
}
编写接口实现类
AdviceImpl.java
package com.zbiti.proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class AdviceImpl implements Advice{
long beginTime = 0;
@Override
public void forwardMethod(Method method) {
System.out.println("end");
beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
@Override
public void backMethod(Method method) {
System.out.println("start");
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(method.getName() + " running time of " + (endTime - beginTime));
}
}
测试
ProxyTest.java
package com.zbiti.proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
public class ProxyTest {
public static void main(String args[]){
//创建目标类的实例对象
ArrayList<String> target = new ArrayList<>();
AdviceImpl adviceImpl = new AdviceImpl();
//创建动态类
Collection proxy = (Collection) getProxy(target, adviceImpl);
proxy.add("aa");
System.out.println(proxy.size());
System.out.println(proxy.getClass().getName());
}
public static Object getProxy(final Object target, final Advice advice){
Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(
target.getClass().getClassLoader(),
target.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new InvocationHandler() {
//动态类通过Invocation类的invoke方法调用目标类所需的方法
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Exception {
advice.forwardMethod(method);
Object retVal = method.invoke(target, args);
advice.backMethod(method);
return retVal;
}
}
);
return proxy;
}
}
结果:
end
start
add running time of 0
end
start
size running time of 0
1
com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0
Process finished with exit code 0Demo2
手动实现一个数据库连接池, 没有使用代理模式的情况下如下:
MyPool.java
package com.zbiti.proxy;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class MyPool {
// 初始化连接数目
private int init_count = 3;
// 最大连接数
private int max_count = 6;
// 记录当前使用连接数
private int current_count = 0;
// 连接池 (存放所有的初始化连接)
private LinkedList<Connection> pool = new LinkedList<Connection>();
//1. 构造函数中,初始化连接放入连接池
public MyPool() {
// 初始化连接
for (int i = 0; i < init_count; i++) {
// 记录当前连接数目
current_count++;
// 创建原始的连接对象
Connection con = createConnection();
// 把连接加入连接池
pool.addLast(con);
}
}
//2. 创建一个新的连接的方法
private Connection createConnection() {
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 原始的目标对象
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.101:3306/cmj", "root", "000000");
return con;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//3. 获取连接
public Connection getConnection() {
// 3.1 判断连接池中是否有连接, 如果有连接,就直接从连接池取出
if (pool.size() > 0) {
return pool.removeFirst();
}
// 3.2 连接池中没有连接: 判断,如果没有达到最大连接数,创建;
if (current_count < max_count) {
// 记录当前使用的连接数
current_count++;
// 创建连接
return createConnection();
}
// 3.3 如果当前已经达到最大连接数,抛出异常
throw new RuntimeException("当前连接已经达到最大连接数目 !");
}
//4. 释放连接
public void realeaseConnection(Connection con) {
// 4.1 判断: 池的数目如果小于初始化连接,就放入池中
if (pool.size() < init_count) {
pool.addLast(con);
} else {
try {
// 4.2 关闭
current_count--;
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
// 测试:
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
MyPool pool = new MyPool();
System.out.println("当前连接: " + pool.current_count); // 3
// 使用连接
pool.getConnection();
pool.getConnection();
Connection con4 = pool.getConnection();
Connection con3 = pool.getConnection();
Connection con2 = pool.getConnection();
Connection con1 = pool.getConnection();
// 释放连接, 连接放回连接池
// pool.realeaseConnection(con1);
/*
* 希望:当关闭连接的时候,要把连接放入连接池!【当调用Connection接口的close方法时候,希望触发pool.addLast(con);操作】把连接放入连接池
* 解决1:实现Connection接口,重写close方法 connection接口方法太多,都实现太麻烦,放弃
* 解决2:动态代理
*/
con1.close();
// 再获取
pool.getConnection();
System.out.println("连接池:" + pool.pool.size()); // 0
System.out.println("当前连接: " + pool.current_count); // 3
}
}
使用代理模式
MyPool2.java
package com.zbiti.proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.LinkedList;
/**
* JDK 动态代理 Object obj = Proxy.newProxyInstance(....);
* 1.参数1:ClassLoader loader ,确定类加载器。程序运行时动态创建类,需要类加载加载到内存。类加载器作用:class文件 --> Class对象
* * 一般情况使用都是当前类的类加载器
* * 类加载器获得方式:MyFactory.class.getClassLoader();
* 2.参数2:Class[] interfaces 代理需要实现的接口们(可能有多个)
* * 方式1:userService.getClass().getInterfaces()【此方式只能在代理对象和接口是父子关系时使用】
* * 方式2:new Class[]{UserService.class}【当被代理对象和其实现接口之间是隔代关系时(即祖孙关系)(即:一个一个列出接口)
* 3.参数3:InvocationHandler h 请求处理类,代理类方法执行时,需要请求处理类来处理。
* * 一般采用匿名内部类:new InvocationHandler(){}
* * 实现方法 invoke ,代理类每一个方法执行一次,将调用一次invoke
* 参数1.1:Object proxy ,代理对象(即 proxyService,不是“代理之前对象”),一般不用。
* 参数2.2:Method method ,当前执行的方法
* * 当前调用方法名:method.getName();
* * 执行目标类方法:Object obj = method.invoke(代理之前对象 , args)
* 参数3.3:Object[] args
* * 当前方法实际参数
*/
public class MyPool2 {
// 初始化连接数目
private int init_count = 3;
// 最大连接数
private int max_count = 6;
// 记录当前使用连接数
private int current_count = 0;
// 连接池 (存放所有的初始化连接)
private LinkedList<Connection> pool = new LinkedList<Connection>();
//1. 构造函数中,初始化连接放入连接池
public MyPool2() {
// 初始化连接
for (int i=0; i<init_count; i++){
// 记录当前连接数目
current_count++;
// 创建原始的连接对象
Connection con = createConnection();
// 把连接加入连接池
pool.addLast(con);
}
}
//2. 创建一个新的连接的方法
private Connection createConnection(){
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 原始的目标对象
final Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.101:3306/cmj", "root", "000000");
/**********对con对象代理**************/
// 对con创建其代理对象
Connection proxy = (Connection) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
con.getClass().getClassLoader(), // 类加载器
//con.getClass().getInterfaces(), // 当目标对象是一个具体的类的时候
new Class[]{Connection.class}, // 目标对象实现的接口
new InvocationHandler() { // 当调用con对象方法的时候, 自动触发事务处理器
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
// 方法返回值
Object result = null;
// 当前执行的方法的方法名
String methodName = method.getName();
// 判断当执行了close方法的时候,把连接放入连接池
if ("close".equals(methodName)) {
System.out.println("begin:当前执行close方法开始!");
// 连接放入连接池
pool.addLast(con);
System.out.println("end: 当前连接已经放入连接池了!");
} else {
// 调用目标对象方法,注意这里不是代理对象
result = method.invoke(con, args);
}
return result;
}
}
);
return proxy;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//3. 获取连接
public Connection getConnection(){
// 3.1 判断连接池中是否有连接, 如果有连接,就直接从连接池取出
if (pool.size() > 0){
return pool.removeFirst();
}
// 3.2 连接池中没有连接: 判断,如果没有达到最大连接数,创建;
if (current_count < max_count) {
// 记录当前使用的连接数
current_count++;
// 创建连接
return createConnection();
}
// 3.3 如果当前已经达到最大连接数,抛出异常
throw new RuntimeException("当前连接已经达到最大连接数目 !");
}
//4. 释放连接
public void realeaseConnection(Connection con) {
// 4.1 判断: 池的数目如果小于初始化连接,就放入池中
if (pool.size() < init_count){
pool.addLast(con);
} else {
try {
// 4.2 关闭
current_count--;
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
// 测试:
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
MyPool2 pool = new MyPool2();
System.out.println("当前连接: " + pool.current_count); // 3
// 使用连接
pool.getConnection();
pool.getConnection();
Connection con4 = pool.getConnection();
Connection con3 = pool.getConnection();
Connection con2 = pool.getConnection();
Connection con1 = pool.getConnection();
// 释放连接, 连接放回连接池
// pool.realeaseConnection(con1);
/*
* 希望:当关闭连接的时候,要把连接放入连接池!【当调用Connection接口的close方法时候,希望触发pool.addLast(con);操作】把连接放入连接池
* 解决1:实现Connection接口,重写close方法
* 解决2:动态代理
*/
con1.close();
// 再获取
pool.getConnection();
System.out.println("连接池:" + pool.pool.size()); // 0
System.out.println("当前连接: " + pool.current_count); // 3
}
}



